- ASIC
- Battery management ICs
- Clocks and timing solutions
- ESD and surge protection devices
- Automotive Ethernet
- Evaluation Boards
- High reliability
- Isolation
- Memories
- Microcontroller
- Power
- RF
- Security and smart card solutions
- Sensor technology
- Small signal transistors and diodes
- Transceivers
- Universal Serial Bus (USB)
- Wireless connectivity
- Search Tools
- Technology
- Packages
- Product Information
- Ordering
- Overview
- Automotive Ethernet Bridges
- Automotive Ethernet PHY for in-vehicle networking
- Automotive Ethernet Switches for in-vehicle networking
- Overview
- Defense
- High-reliability custom services
- NewSpace
- Space
- Overview
- Embedded flash IP solutions
- Flash+RAM MCP solutions
- F-RAM (Ferroelectric RAM)
- NOR flash
- nvSRAM (non-volatile SRAM)
- PSRAM (Pseudostatic RAM)
- Radiation hardened and high-reliability memories
- SRAM (static RAM)
- Wafer and die memory solutions
- Overview
- 32-bit FM Arm® Cortex® Microcontroller
- 32-bit AURIX™ TriCore™ microcontroller
- 32-bit PSOC™ Arm® Cortex® microcontroller
- 32-bit TRAVEO™ T2G Arm® Cortex® microcontroller
- 32-bit XMC™ industrial microcontroller Arm® Cortex®-M
- Legacy microcontroller
- Motor control SoCs/SiPs
- Sensing controllers
- Overview
- AC-DC power conversion
- Automotive conventional powertrain ICs
- Class D audio amplifier ICs
- Contactless power and sensing ICs
- DC-DC converters
- Diodes and thyristors (Si/SiC)
- Gallium nitride (GaN)
- Gate driver ICs
- IGBTs – Insulated gate bipolar transistors
- Intelligent power modules (IPM)
- LED driver ICs
- Motor drivers
- Power MOSFETs
- Power modules
- Power supply ICs
- Protection and monitoring ICs
- Silicon carbide (SiC)
- Smart power switches
- Solid state relays
- Wireless charging ICs
- Overview
- Antenna cross switches
- Antenna tuners
- Bias and control
- Coupler
- Driver amplifiers
- High Reliability Discrete
- Low noise amplifiers (LNAs)
- RF diode
- RF switches
- RF transistors
- Wireless control receiver
- Overview
- Calypso® products
- CIPURSE™ products
- Contactless memories
- OPTIGA™ embedded security solutions
- SECORA™ security solutions
- Security controllers
- Smart card modules
- Smart solutions for government ID
- Overview
- ToF 3D image sensors
- Current sensors
- Gas sensors
- Inductive position sensors
- MEMS microphones
- Pressure sensors
- Radar sensors
- Magnetic position sensors
- Magnetic speed sensors
- Overview
- Bipolar transistors
- Diodes
- Small signal/small power MOSFET
- Overview
- Automotive transceivers
- Control communication
- Powerline communications
- Overview
- USB 2.0 peripheral controllers
- USB 3.2 peripheral controllers
- USB hub controllers
- USB PD high-voltage microcontrollers
- USB-C AC-DC and DC-DC charging solutions
- USB-C charging port controllers
- USB-C Power Delivery controllers
- Overview
- AIROC™ Automotive wireless
- AIROC™ Bluetooth® and multiprotocol
- AIROC™ connected MCU
- AIROC™ Wi-Fi + Bluetooth® combos
- Overview
- Commercial off-the-shelf (COTs) memory portfolio
- Defense memory portfolio
- High-reliability power conversion and management
- Overview
- Rad hard microwave and RF
- Radiation hardened power
- Space memory portfolio
- Overview
- Parallel NOR flash
- SEMPER™ NOR flash family
- SEMPER™ X1 LPDDR flash
- Serial NOR flash
- Overview
- FM0+ 32-bit Arm® Cortex®-M0+ microcontroller (MCU) families
-
FM3 32-bit Arm® Cortex®-M3 microcontroller (MCU) families
- Overview
- FM3 CY9AFx1xK series Arm® Cortex®-M3 microcontroller (MCU)
- FM3 CY9AFx1xL/M/N series Arm® Cortex®-M3 microcontroller (MCU)
- FM3 CY9AFx2xK/L series Arm® Cortex®-M3 microcontroller (MCU)
- FM3 CY9AFx3xK/L series ultra-low leak Arm® Cortex®-M3 microcontroller (MCU)
- FM3 CY9AFx4xL/M/N series low power Arm® Cortex®-M3 microcontroller (MCU)
- FM3 CY9AFx5xM/N/R series low power Arm® Cortex®-M3 microcontroller (MCU)
- FM3 CY9AFxAxL/M/N series ultra-low leak Arm® Cortex®-M3 microcontroller (MCU)
- FM3 CY9BFx1xN/R high-performance series Arm® Cortex®-M3 microcontroller (MCU)
- FM3 CY9BFx1xS/T high-performance series Arm® Cortex®-M3 microcontroller (MCU)
- FM3 CY9BFx2xJ series Arm® Cortex®-M3 microcontroller (MCU)
- FM3 CY9BFx2xK/L/M series Arm® Cortex®-M3 microcontroller (MCU)
- FM3 CY9BFx2xS/T series Arm® Cortex®-M3 microcontroller (MCU)
-
FM4 32-bit Arm® Cortex®-M4 microcontroller (MCU) families
- Overview
- FM4 CY9BFx6xK/L high-performance series Arm® Cortex®-M4F microcontroller (MCU)
- FM4 CY9BFx6xM/N/R high-performance series Arm® Cortex®-M4F microcontroller (MCU)
- FM4 S6E2C high-performance series Arm® Cortex®-M4F microcontroller (MCU)
- FM4 S6E2G series connectivity Arm® Cortex®-M4F microcontroller (MCU)
- FM4 S6E2H high-performance series Arm® Cortex®-M4F microcontroller (MCU)
- Overview
-
32-bit TriCore™ AURIX™ – TC2x
- Overview
- AURIX™ family – TC21xL
- AURIX™ family – TC21xSC (wireless charging)
- AURIX™ family – TC22xL
- AURIX™ family – TC23xL
- AURIX™ family – TC23xLA (ADAS)
- AURIX™ family – TC23xLX
- AURIX™ family – TC264DA (ADAS)
- AURIX™ family – TC26xD
- AURIX™ family – TC27xT
- AURIX™ family – TC297TA (ADAS)
- AURIX™ family – TC29xT
- AURIX™ family – TC29xTT (ADAS)
- AURIX™ family – TC29xTX
- AURIX™ TC2x emulation devices
-
32-bit TriCore™ AURIX™ – TC3x
- Overview
- AURIX™ family - TC32xLP
- AURIX™ family – TC33xDA
- AURIX™ family - TC33xLP
- AURIX™ family – TC35xTA (ADAS)
- AURIX™ family – TC36xDP
- AURIX™ family – TC37xTP
- AURIX™ family – TC37xTX
- AURIX™ family – TC38xQP
- AURIX™ family – TC39xXA (ADAS)
- AURIX™ family – TC39xXX
- AURIX™ family – TC3Ex
- AURIX™ TC37xTE (emulation devices)
- AURIX™ TC39xXE (emulation devices)
- 32-bit TriCore™ AURIX™ – TC4x
- Overview
- PSOC™ 4 Arm® Cortex®-M0/M0+
- PSOC™ 4 HV Arm® Cortex®-M0+
- PSOC™ 5 LP Arm® Cortex®-M3
- PSOC™ 6 Arm® Cortex®-M4/M0+
- PSOC™ Multitouch Touchscreen Controller
- PSOC™ Control C3 Arm® Cortex®-M33
- PSOC™ Automotive 4: Arm® Cortex®-M0/M0+
- PSOC™ Edge Arm® Cortex® M55/M33
- Overview
- 32-bit TRAVEO™ T2G Arm® Cortex® for body
- 32-bit TRAVEO™ T2G Arm® Cortex® for cluster
- Overview
- 32-bit XMC1000 industrial microcontroller Arm® Cortex®-M0
- 32-bit XMC4000 industrial microcontroller Arm® Cortex®-M4
- XMC5000 Industrial Microcontroller Arm® Cortex®-M4F
- 32-bit XMC7000 Industrial Microcontroller Arm® Cortex®-M7
- Overview
- Legacy 32-bit MCU
- Legacy 8-bit/16-bit microcontroller
- Other legacy MCUs
- Overview
- AC-DC integrated power stage - CoolSET™
- AC-DC PWM-PFC controller
- Overview
- Bridge rectifiers & AC switches
- CoolSiC™ Schottky diodes
- Diode bare dies
- Silicon diodes
- Thyristor / Diode Power Modules
- Thyristor soft starter modules
- Thyristor/diode discs
- Overview
- Automotive gate driver ICs
- Isolated Gate Driver ICs
- Gate driver ICs for GaN HEMTs
- Level-Shift Gate Driver ICs
- Low-Side Drivers
- Transformer Driver ICs
- Overview
- AC-DC LED driver ICs
- Ballast IC
- DC-DC LED driver IC
- LED dimming interface IC
- Linear LED driver IC
- LITIX™ - Automotive LED Driver IC
- NFC wireless configuration IC with PWM output
- VCSEL driver
- Overview
- BLDC motor drivers
- BDC motor drivers
- Stepper & servo motor drivers
- Motor drivers with MCU
- Bridge drivers with MOSFETs
- Gate driver ICs
- Overview
- Automotive MOSFET
- Dual MOSFETs
- MOSFET (Si & SiC) Modules
- N-channel depletion mode MOSFET
- N-channel MOSFETs
- P-channel MOSFETs
- Silicon carbide CoolSiC™ MOSFETs
- Small signal/small power MOSFET
- Overview
- Automotive transceivers
- Linear Voltage Regulators for Automotive Applications
- OPTIREG™ PMIC
- OPTIREG™ switcher
- OPTIREG™ System Basis Chips (SBC)
- Overview
- eFuse
-
High-side switches
- Overview
- Classic PROFET™ 12V | Automotive smart high-side switch
- Classic PROFET™ 24V | Automotive smart high-side switch
- Power PROFET™ + 12/24/48V | Automotive smart high-side switch
- PROFET™ + 12V | Automotive smart high-side switch
- PROFET™ + 24V | Automotive smart high-side switch
- PROFET™ + 48V | Automotive smart high-side switch
- PROFET™ +2 12V | Automotive smart high-side switch
- PROFET™ Industrial | Smart high-side switch
- PROFET™ Wire Guard 12V | Automotive eFuse
- Low-side switches
- Multichannel SPI Switches & Controller
- Overview
- Radar sensors for automotive
- Radar sensors for IoT
- Overview
- EZ-USB™ CX3 MIPI CSI2 to USB 3.0 camera controller
- EZ-USB™ FX10 & FX5N USB 10Gbps peripheral controller
- EZ-USB™ FX20 USB 20 Gbps peripheral controller
- EZ-USB™ FX3 USB 5 Gbps peripheral controller
- EZ-USB™ FX3S USB 5 Gbps peripheral controller with storage interface
- EZ-USB™ FX5 USB 5 Gbps peripheral controller
- EZ-USB™ SD3 USB 5 Gbps storage controller
- EZ-USB™ SX3 FIFO to USB 5 Gbps peripheral controller
- Overview
- EZ-PD™ CCG3 USB type-C port controller PD
- EZ-PD™ CCG3PA USB-C and PD
- EZ-PD™ CCG3PA-NFET USB-C PD controller
- EZ-PD™ CCG7x consumer USB-C Power Delivery & DC-DC controller
- EZ-PD™ PAG1: power adapter generation 1
- EZ-PD™ PAG2: Power Adapter Generation 2
- EZ-PD™ PAG2-PD USB-C PD Controller
- Overview
- EZ-PD™ ACG1F one-port USB-C controller
- EZ-PD™ CCG2 USB Type-C port controller
- EZ-PD™ CCG3PA Automotive USB-C and Power Delivery controller
- EZ-PD™ CCG4 two-port USB-C and PD
- EZ-PD™ CCG5 dual-port and CCG5C single-port USB-C PD controllers
- EZ-PD™ CCG6 one-port USB-C & PD controller
- EZ-PD™ CCG6_CFP and EZ-PD™ CCG8_CFP Dual-Single-Port USB-C PD
- EZ-PD™ CCG6DF dual-port and CCG6SF single-port USB-C PD controllers
- EZ-PD™ CCG7D Automotive dual-port USB-C PD + DC-DC controller
- EZ-PD™ CCG7S Automotive single-port USB-C PD solution with a DC-DC controller + FETs
- EZ-PD™ CCG7SAF Automotive Single-port USB-C PD + DC-DC Controller + FETs
- EZ-PD™ CCG8 dual-single-port USB-C PD
- EZ-PD™ CMG1 USB-C EMCA controller
- EZ-PD™ CMG2 USB-C EMCA controller with EPR
- LATEST IN
- Aerospace and defense
- Automotive
- Consumer electronics
- Health and lifestyle
- Home appliances
- Industrial
- Information and Communication Technology
- Renewables
- Robotics
- Security solutions
- Smart home and building
- Solutions
- Overview
- Defense applications
- Space applications
- Overview
- 48 V systems for EVs & mild hybrids
- ADAS & autonomous driving
- Automotive body electronics & power distribution
- Automotive LED lighting systems
- Chassis control & safety
- Electric vehicle drivetrain system
- EV thermal management system
- Internal combustion drivetrain systems
- In-vehicle infotainment & HMI
- Light electric vehicle solutions
- Overview
- Power adapters and chargers
- Complete system solutions for smart TVs
- Mobile device and smartphone solutions
- Multicopters and drones
- Power tools
- Semiconductor solutions for home entertainment applications
- Smart conference systems
- Overview
- Adapters and chargers
- Asset Tracking
- Battery formation and testing
- Electric forklifts
- Battery energy storage (BESS)
- EV charging
- High voltage solid-state power distribution
- Industrial automation
- Industrial motor drives and controls
- Industrial robots system solutions for Industry 4.0
- LED lighting system design
- Light electric vehicle solutions
- Power tools
- Power transmission and distribution
- Traction
- Uninterruptible power supplies (UPS)
- Overview
- Data center and AI data center solutions
- Edge computing
- Telecommunications infrastructure
- Machine Learning Edge AI
- Overview
- Battery formation and testing
- EV charging
- Hydrogen
- Photovoltaic
- Wind power
- Solid-state circuit breaker
- Battery energy storage (BESS)
- Overview
- Device authentication and brand protection
- Embedded security for the Internet of Things (IoT)
- eSIM applications
- Government identification
- Mobile security
- Payment solutions
- Access control and ticketing
- Overview
- Domestic robots
- Heating ventilation and air conditioning (HVAC)
- Home and building automation
- PC accessories
- Semiconductor solutions for home entertainment applications
- Overview
- Battery management systems (BMS)
- Connectivity
- Human Machine Interface
- Machine Learning Edge AI
- Motor control
- Power conversion
- Security
- Sensor solutions
- System diagnostics and analytics
- Overview
- Automotive auxiliary systems
- Automotive gateway
- Automotive power distribution
- Body control modules (BCM)
- Comfort & convenience electronics
- Zonal DC-DC converter 48 V-12 V
- Zone control unit
- Overview
- Automotive animated LED lighting system
- Automotive LED front single light functions
- Automotive LED rear single light functions
- Full LED headlight system - multi-channel LED driver
- LED drivers (electric two- & three-wheelers)
- LED pixel light controller - supply & communication
- Static interior ambient LED light
- Overview
- Active suspension control
- Airbag system
- Automotive braking solutions
- Automotive steering solutions
- Chassis domain control
- Reversible seatbelt pretensioner
- Overview
-
Automotive BMS
- Overview
- Automotive battery cell monitoring & balancing
- Automotive battery control unit (BCU)
- Automotive battery isolated communication
- Automotive battery management system (BMS) - 12 V to 24 V
- Automotive battery management system (BMS) - 48 V
- Automotive battery management system (BMS) - high-voltage
- Automotive battery pack monitoring
- Automotive battery passport & event logging
- Automotive battery protection & disconnection
- Automotive current sensing & coulomb counting
- BMS (electric two- & three-wheelers)
- EV charging
- EV inverters
- EV power conversion & OBC
- FCEV powertrain system
- Overview
- Automatic transmission hydraulic system
- Belt starter generator 48 V – inverter ISG
- Diesel direct injection
- Double-clutch transmission electrical control
- Double-clutch transmission hydraulic control
- Gasoline direct injection
- Multi-port fuel injection
- Small 1-cylinder combustion engine solution
- Small engine starter kit
- Transfer case brushed DC
- Transfer case brushless DC (BLDC)
- Overview
- Automotive head unit
- Automotive USB-C power & data solution
- Automotive instrument cluster
- Automotive telematics control unit (TCU)
- Center information display (CID)
- High-performance cockpit controller
- In-cabin wireless charging
- Smart instrument cluster (electric two- & three-wheelers)
- Overview
- E-bike solutions
- Two- & three-wheeler solutions
- Overview
- Audio amplifier solutions
- Complete system solutions for smart TVs
- Distribution audio amplifier unit solutions
- Home theater installation speaker system solutions
- Party speaker solutions
- PoE audio amplifier unit solutions
- Portable speaker solutions
- Powered active speaker systems
- Remote control
- Smart speaker designs
- Soundbar solutions
- Overview
- Data center and AI data center solutions
- Digital input/output (I/O) modules
- DIN rail power supply solutions
- Home and building automation
- Industrial HMI Monitors and Panels
- Industrial motor drives and controls
- Industrial PC
- Industrial robots system solutions for Industry 4.0
- Machine vision
- Mobile robots (AGV, AMR)
- Programmable logic controller (PLC)
- Solid-state circuit breaker
- Uninterruptible power supplies (UPS)
- Overview
- 48 V intermediate bus converter (IBC)
- AI accelerator cards
- AMD server CPUs
- Ampere CPUs
- FPGAs in datacenter applications
- Intel server CPUs
- Networking and switch platforms
- Power path protection
- Power system reliability modeling
- RAID storage
- Server battery backup units (BBU)
- Server power supply
- SmartNIC cards
- Overview
- AC-DC power conversion for telecommunications infrastructure
- DC-DC power conversion for telecommunications infrastructure
- FPGA in wired and wireless telecommunications applications
- Satellite communications
- Power system reliability modeling
- RF front end components for telecommunications infrastructure
- Overview
-
AC-DC power conversion
- Overview
- AC-DC auxiliary power supplies
- AC-DC power conversion for telecommunications infrastructure
- Adapters and chargers
- Automotive LED lighting systems
- Complete system solutions for smart TVs
- Desktop power supplies
- EV charging
- Industrial power supplies
- PoE power sourcing equipment (PSE)
- Server power supply units (PSU)
- Uninterruptible power supplies (UPS)
- DC-DC power conversion
- Overview
- Power supply health monitoring
- LATEST IN
- Digital documentation
- Evaluation boards
- Finder & selection tools
- Platforms
- Services
- Simulation & Modeling
- Software
- Tools
- Partners
- Infineon for Makers
- University Alliance Program
- Overview
- Bipolar Discs Finder
- Bipolar Module Finder
- Connected Secure Systems Finder
- Diode Rectifier Finder
- ESD Protection Finder
- Evaluation Board Finder
- Gate Driver Finder
- IGBT Discrete Finder
- IGBT Module Finder
- IPM Finder
- Microcontroller Finder
- MOSFET Finder
- PMIC Finder
- Product Finder
- PSOC™ and FMx MCU Board & Kit Finder
- Radar Finder
- Reference Design Finder
- Simulation Model Finder
- Smart Power Switch Finder
- Transceiver Finder
- Voltage Regulator Finder
- Wireless Connectivity Board & Kit Finder
- Overview
- AIROC™ software & tools
- AURIX™ software & tools
- DRIVECORE for automotive software development
- iMOTION™ software & tools
- Infineon Smart Power Switches & Gate Driver Tool Suite
- MOTIX™ software & tools
- OPTIGA™ software & tools
- PSOC™ software & tools
- TRAVEO™ software & tools
- XENSIV™ software & tools
- XMC™ software & tools
- Overview
- CoolGaN™ Simulation Tool (PLECS)
- HiRel Fit Rate Tool
- Infineon Designer
- Interactive product sheet
- IPOSIM Online Power Simulation Platform
- InfineonSpice Offline Simulation Tool
- OPTIREG™ automotive power supply ICs Simulation Tool (PLECS)
- Power MOSFET Simulation Models
- PowerEsim Switch Mode Power Supply Design Tool
- Solution Finder
- XENSIV™ Magnetic Sensor Simulation Tool
- Overview
- AURIX™ certifications
- AURIX™ development tools
-
AURIX™ Embedded Software
- Overview
- AURIX™ Applications software
- AURIX™ Artificial Intelligence
- AURIX™ Gateway
- AURIX™ iLLD Drivers
- Infineon safety
- AURIX™ Security
- AURIX™ TC3xx Motor Control Application Kit
- AURIX™ TC4x SW application architecture
- Infineon AUTOSAR
- Communication and Connectivity
- Middleware
- Non AUTOSAR OS/RTOS
- OTA
- AURIX™ Microcontroller Kits
- Overview
- TRAVEO™ Development Tools
- TRAVEO™ Embedded Software
- Overview
- XENSIV™ Development Tools
- XENSIV™ Embedded Software
- XENSIV™ evaluation boards
- Overview
- CAPSENSE™ Controllers Code Examples
- Memories for Embedded Systems Code Examples
- PSOC™ 1 Code Examples for PSOC™ Designer
- PSOC™ 3 Code Examples for PSOC™ Creator
- PSOC™ 3/4/5 Code Examples
- PSOC™ 4 Code Examples for PSOC™ Creator
- PSOC™ 6 Code Examples for PSOC™ Creator
- PSOC™ 63 Code Examples
- USB Controllers Code Examples
- Overview
- DEEPCRAFT™ AI Hub
- DEEPCRAFT™ Audio Enhancement
- DEEPCRAFT™ Model Converter
-
DEEPCRAFT™ Ready Models
- Overview
- DEEPCRAFT™ Ready Model for Baby Cry Detection
- DEEPCRAFT™ Ready Model for Cough Detection
- DEEPCRAFT™ Ready Model for Direction of Arrival (Sound)
- DEEPCRAFT™ Ready Model for Factory Alarm Detection
- DEEPCRAFT™ Ready Model for Fall Detection
- DEEPCRAFT™ Ready Model for Gesture Classification
- DEEPCRAFT™ Ready Model for Siren Detection
- DEEPCRAFT™ Ready Model for Snore Detection
- DEEPCRAFT™ Studio
- DEEPCRAFT™ Voice Assistant
- Overview
- AIROC™ Wi-Fi & Bluetooth EZ-Serial Module Firmware Platform
- AIROC™ Wi-Fi & Bluetooth Linux and Android Drivers
- emWin Graphics Library and GUI for PSOC™
- Infineon Complex Device Driver for Battery Management Systems
- Memory Solutions Hub
- PSOC™ 6 Peripheral Driver Library (PDL) for PSOC™ Creator
- USB Controllers EZ-USB™ GX3 Software and Drivers
- Overview
- CAPSENSE™ Controllers Configuration Tools EZ-Click
- DC-DC Integrated POL Voltage Regulators Configuration Tool – PowIRCenter
- EZ-USB™ SX3 Configuration Utility
- FM+ Configuration Tools
- FMx Configuration Tools
- Tranceiver IC Configuration Tool
- USB EZ-PD™ Configuration Utility
- USB EZ-PD™ Dock Configuration Utility
- USB EZ-USB™ HX3C Blaster Plus Configuration Utility
- USB UART Config Utility
- XENSIV™ Tire Pressure Sensor Programming
- Overview
- EZ-PD™ CCGx Dock Software Development Kit
-
FMx Softune IDE
- Overview
- RealOS™ Real-Time Operating System
- Softune IDE Language tools
- Softune Workbench
- Tool Lineup for F2MC-16 Family SOFTUNE V3
- Tool Lineup for F2MC-8FX Family SOFTUNE V3
- Tool Lineup for FR Family SOFTUNE V6
- Virtual Starter Kit
- Windows 10 operation of released SOFTUNE product
- Windows 7 operation of released SOFTUNE product
- Windows 8 operation of released SOFTUNE product
- ModusToolbox™ Software
- PSOC™ Creator Software
- Radar Development Kit
- RUST
- USB Controllers SDK
- Wireless Connectivity Bluetooth Mesh Helper Applications
- XMC™ DAVE™ Software
- Overview
- AIROC™ Bluetooth® Connect App Archive
- Cypress™ Programmer Archive
- EZ-PD™ CCGx Power Software Development Kit Archive
- ModusToolbox™ Software Archive
- PSOC™ Creator Archive
- PSOC™ Designer Archive
- PSOC™ Programmer Archive
- USB EZ-PD™ Configuration Utility Archives
- USB EZ-PD™ Host SDK Archives
- USB EZ-USB™ FX3 Archive
- USB EZ-USB™ HX3PD Configuration Utility Archive
- WICED™ Smart SDK Archive
- WICED™ Studio Archive
- Overview
- Infineon Developer Center Launcher
- Infineon Register Viewer
- Pin and Code Wizard
- Timing Solutions
- Wireless Connectivity
- LATEST IN
- Support
- Training
- Developer Community
- News
Business & Financial Press
Feb 23, 2026
Business & Financial Press
Feb 19, 2026
Business & Financial Press
Feb 19, 2026
Business & Financial Press
Feb 19, 2026
- Company
- Our stories
- Events
- Press
- Investor
- Careers
- Quality
- Latest news
Business & Financial Press
Feb 23, 2026
Business & Financial Press
Feb 19, 2026
Business & Financial Press
Feb 19, 2026
Business & Financial Press
Feb 19, 2026

The future of charging electric vehicles
Electric vehicles promote sustainable mobility, but for full decarbonization, key factors include renewable energy, affordability, extensive charging networks, and fast charging. Infineon contributes to a clean, safe, and smart charging infrastructure.
Jul 10, 2025
Infineon's power electronics pave the way for efficient charging networks and decarbonization
Battery-powered electric vehicles are driving sustainable mobility, from e-bikes to heavy-duty trucks. However, in order to leverage the opportunities of electro-mobility, several conditions must be met:
Not only does the electricity have to come from renewable sources, but the vehicles also have to be affordable. It is also crucial that charging points are available in a comprehensive network and the charging times are short and comparable to refueling a vehicle today. As the market leader in power electronics Infineon is a key enabler here, helping to make ubiquitous and energy-efficient charging infrastructures a reality.
Driving the expansion of vital charging infrastructure
The charging infrastructure for electric cars, trucks and buses is making substantial strides. Remarkable progress has been made globally, with more than 12 million public charging points installed in 2024, thereof about 10 million in Greater China, approximately 1.7 million in Europe and about 430,000 in North America.
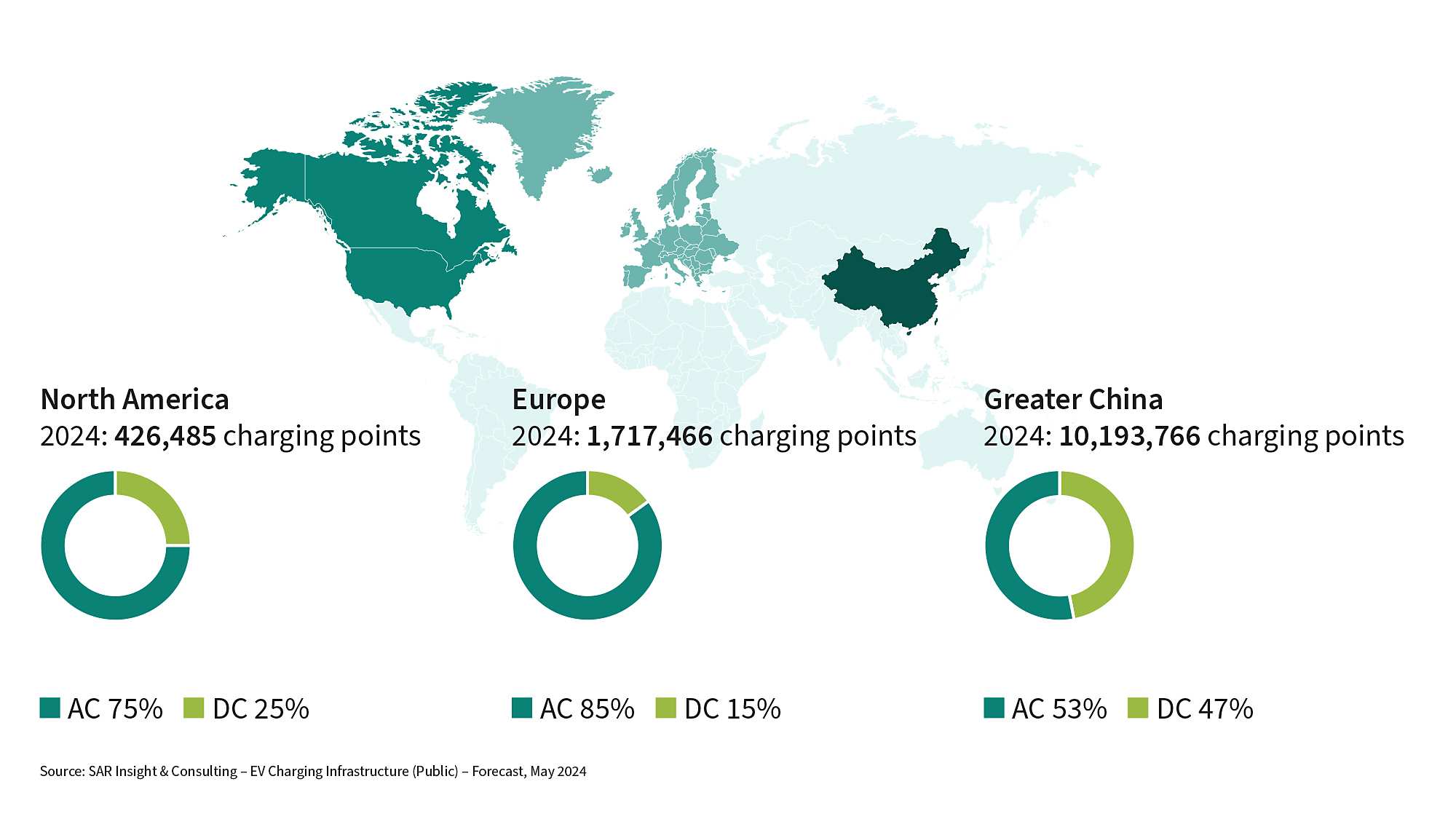
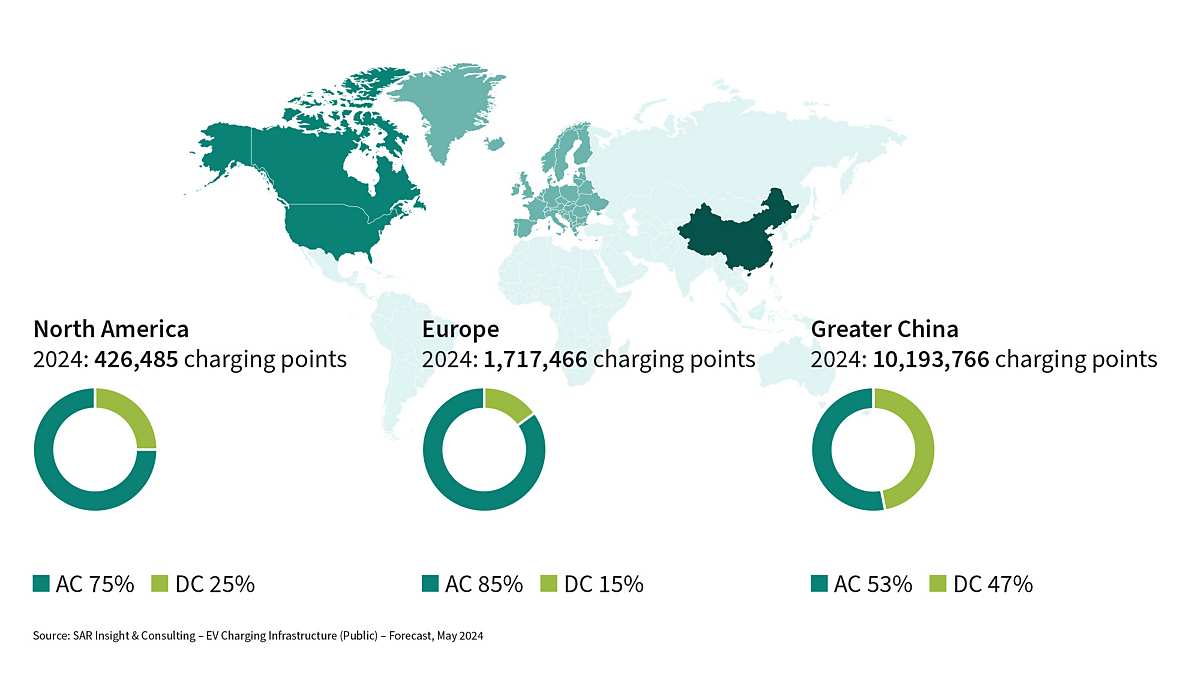

In the coming years, a broad network of energy-efficient and fast-charging infrastructures will be a main factor in achieving electrification targets in transportation. Regional government initiatives aim to define and install public charging infrastructures with interoperable payment solutions to give users a seamless experience and clean mobility.
At the same time, charging points as well as the vehicles themselves have to operate and charge as energy-efficiently as possible. The type of charging station depends on where users charge and how much time they have – whether at home, at work or on the go.
Infineon products and solutions such as SiC-based devices are key to fast charging. Our range of complete one-stop-shop solutions and discretes covers the entire product spectrum, including power conversion, microcontrollers, security and auxiliary power supplies and even communication.
Either direct current (DC) or alternating current (AC) can be used to charge an electric car. But, since the battery in an electric car needs direct current, alternating current has to be converted. There are two charging modes, depending on where the conversion to DC occurs: on-board and off-board, both of which have their advantages in terms of speed (DC charging) and lower costs (AC charging).
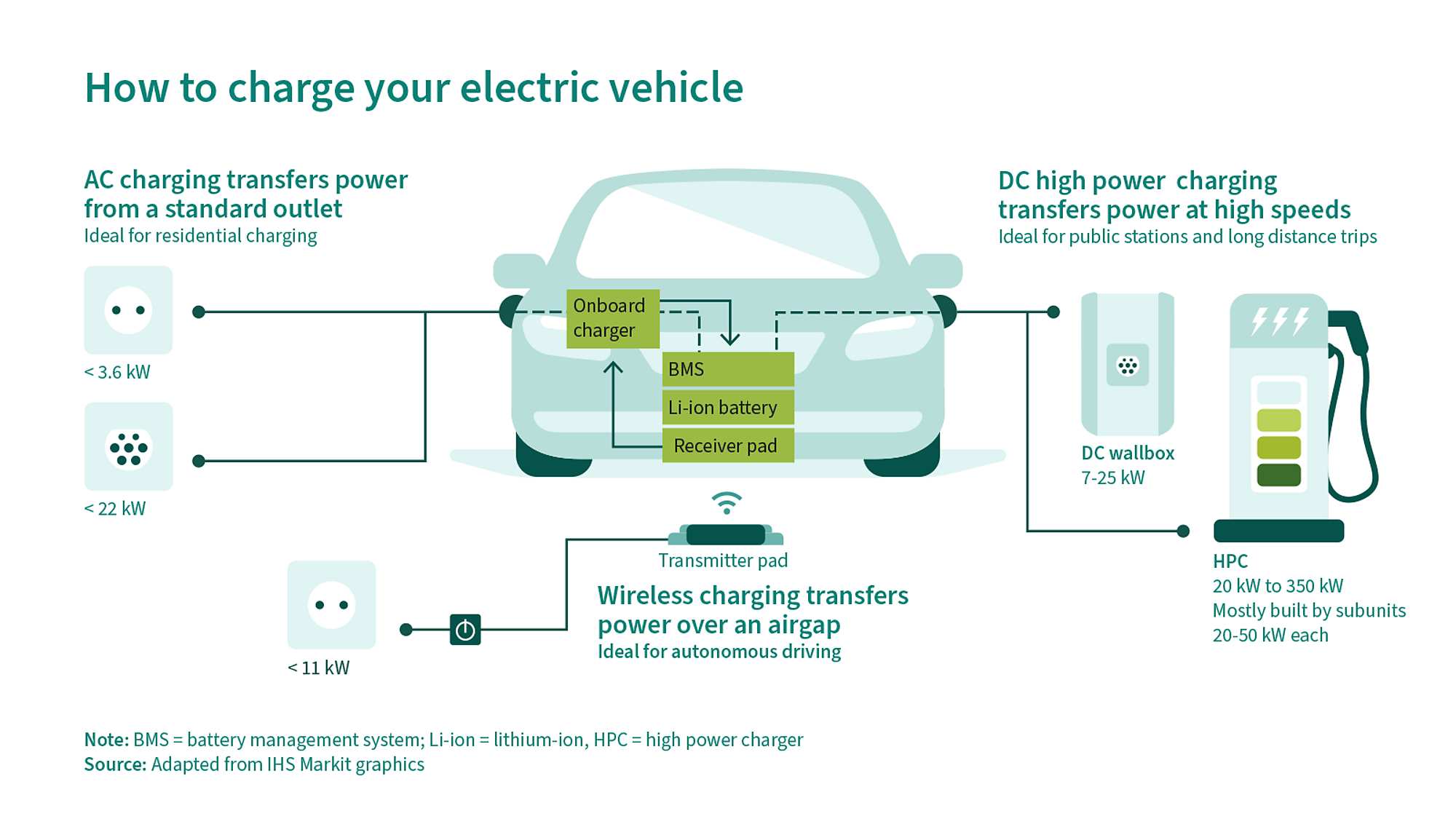
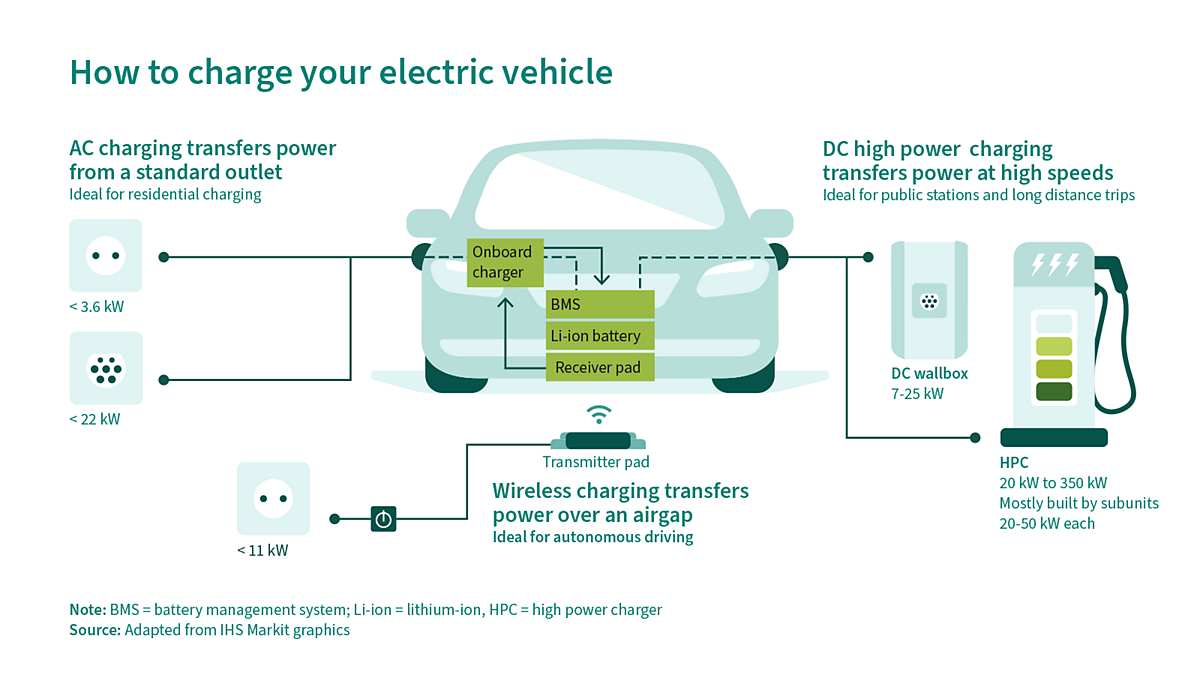
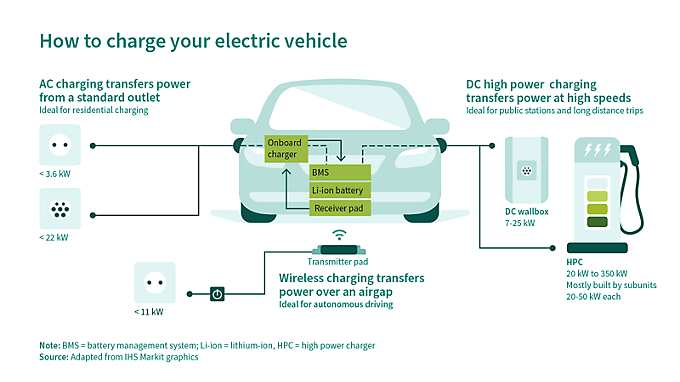
AC chargers feed AC power from the outlet or charging station into the vehicle, where the on-board charger converts it to DC power in order to charge the battery. Conversely, DC offboard chargers internally convert AC power to DC power and then deliver it to the vehicle to charge the battery directly
Infineon semiconductors drive both on-board and off-board charging designs. Whether discretes or modules, based on conventional silicon-based (Si) or cutting edge SiC topologies, our customers can choose from the wide portfolio of the leading power semiconductor supplier to drive the expansion of the EV charging infrastructure.
The choice of charging method depends on various factors, including the available infrastructure, the time you have for charging, your vehicle's battery capacity, and your personal preferences.
- Charging at home
For home charging, in most cases homeowners install a charging station (wall box) in the garage or somewhere outside the house. They just have to connect the charging cable and the electric car will charge overnight. The trend here is solar power: More and more homeowners are using the solar power from their roofs to recharge their electric cars. They use a photovoltaic system, a charging station and an energy management system. Adding an energy storage unit helps establish independence from charging in the daytime, when there is a lot of light. - Public charging on the go
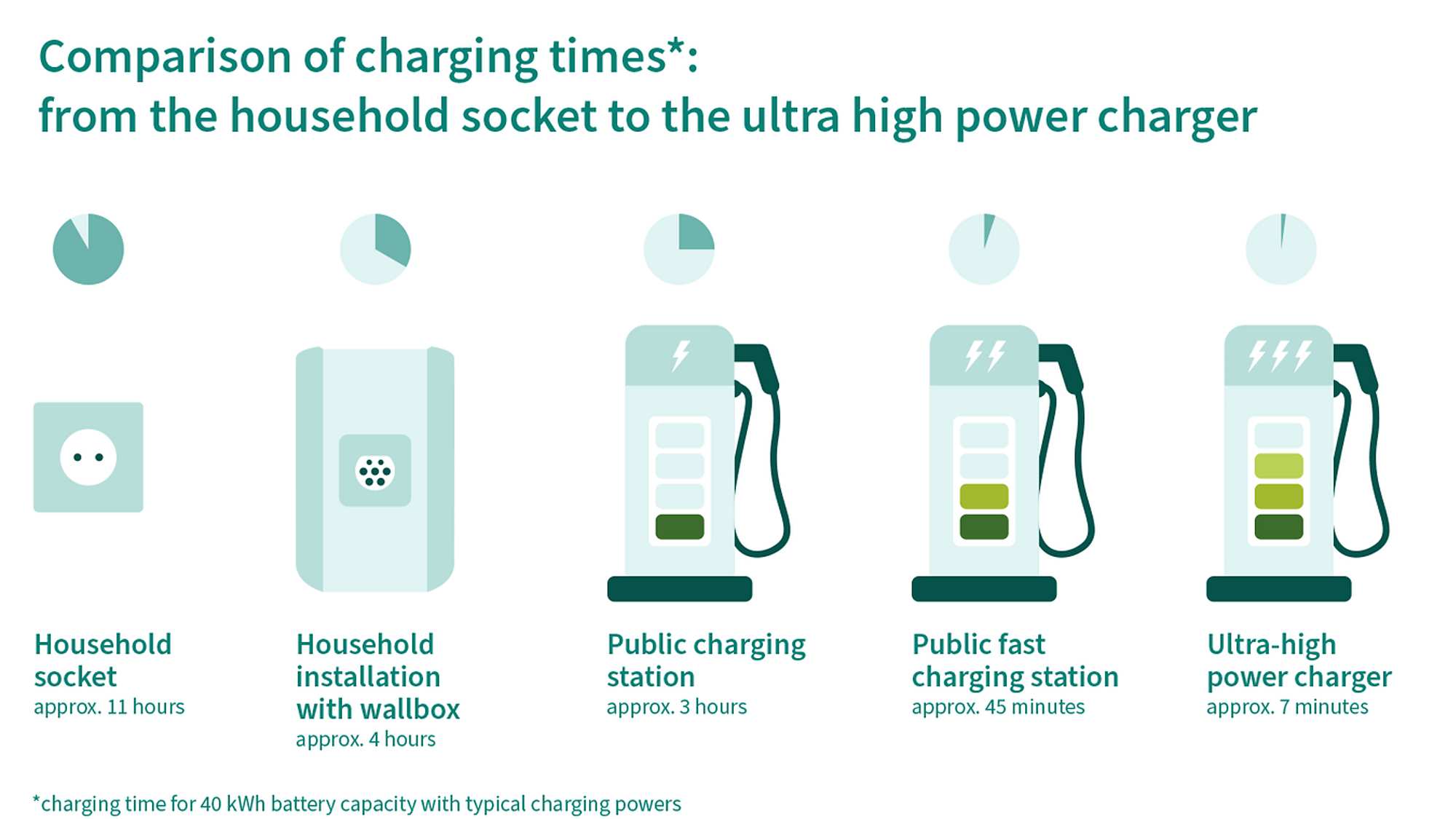
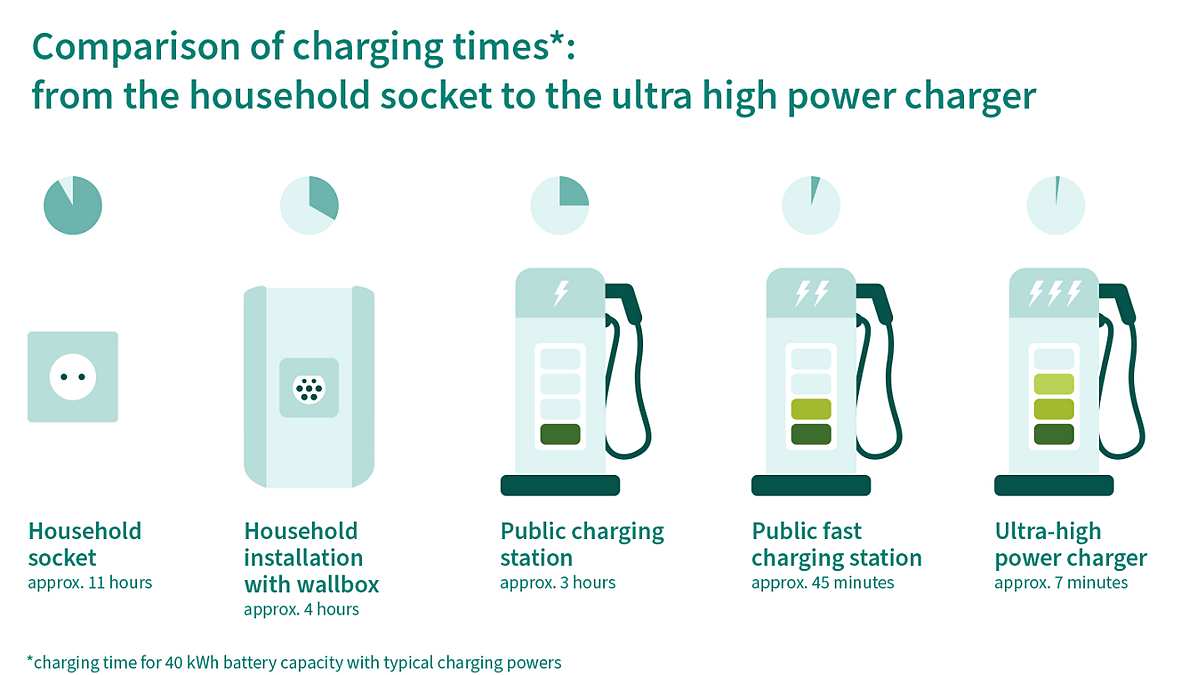
Particularly on long business trips or journeys, there is a need to use the public charging infrastructure, e.g. on highways. In this case, charging speed is crucial. Today, a typical electric car can already charge about 80% of its battery capacity in less than 10 minutes. This is not much longer than refueling a conventional car with an internal combustion engine. - Charging at work
Another option is charging at work when the employer provides a charging infrastructure. Car users only need their own charging cable.

Suitable semiconductors for all types of electric vehicles
Infineon is a member of the CharIN initiative (Charging Interface Initiative e.V.). The goals of this global initiative are to develop, establish and promote a global charging infrastructure standard for all types of battery-powered electric vehicles.
Infineon’s semiconductor solutions are suitable for all types of electric vehicles: pure electric vehicles, plug-in hybrid vehicles and mild hybrid vehicles with 48-volt technology. Last but not least, Infineon components also cover vehicles based on emerging hydrogen technology.
Integrated Infineon components are the core building blocks of controllers and systems that are typical of electric cars: on-board charger, DC-DC converter, battery management unit, drivetrain controller, electric braking system as well as power steering, air conditioning, thermal management, rear light control, windshield wipers and window lifts. These components rely on the following product families: HybridPACK™ Drive power modules, AURIX™ microcontrollers, EiceDRIVER™ driver ICs and many other Infineon sensors, microcontrollers, power semiconductors and Wi-Fi®/Bluetooth® connectivity solutions.
Explore our portfolio for electromobility applications: