
Smart travel in urban areas
Shaping smart cities with smart mobility services
Mobility services in smart cities have one paramount purpose: To make life easier for travelers. A key factor here is to increase individual convenience, which increasingly involves Mobility as a Service (MaaS). This includes the focus on public transportation and sharing options for cars and electric light vehicles such as e-scooters, eventually decreasing the use of individually owned cars.
Most critical for MaaS offerings is how well they mesh with each other. Infineon semiconductor solutions enable the rise of MaaS and are built on open standards, highest safety levels, trusted payments solutions, and breakthrough technologies such as ultra-wideband.

MaaS is the integration of various forms of transport services into one single mobility platform allowing mobility on demand. This means that different operators no longer have to think in single categories such as “train”, “bus” or “car”. They offer mobility services as a combined, multimodal service on one platform. To do this, they must, for example, offer joint booking payment applications and concur on seamless route planning across all modes of transport. In recent years, public transport operators (PTO), car manufacturers, rental companies and platform developers have increasingly extended their offerings on the market, thinking more and more end-to-end – from the first to the last step of every passenger journey.
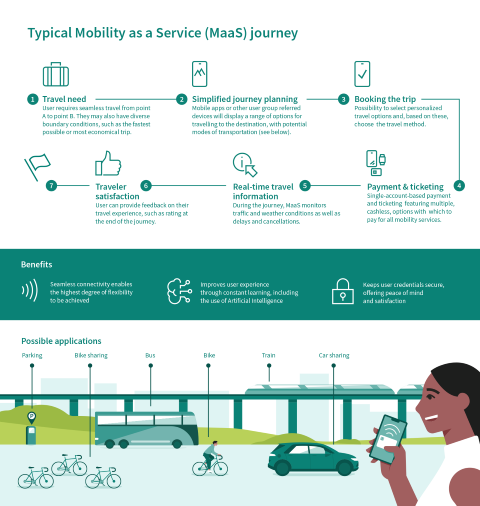
Typical MaaS user journey
A gateway for a seamless travel experience
With more advanced MaaS, city dwellers will book their journeys easily using an app. The app takes care of the first and last step of every passenger journey, offering multimodal transport options through one simple ‘on-demand’ booking and payment application.
According to McKinsey, these seamless mobility options are cleaner, more convenient and more efficient than the status quo, accommodating up to 30 percent more traffic while cutting travel time by 10 percent. To make MaaS appealing and encourage adoption, Infineon has determined four gateways for a range of consumer services: identification, payment, access control and ticketing. In this context, overall convergence and open ticketing standards are the key for the best possible user experience. In contrast to the automotive industry, these features require different safety and qualification standards placing more responsibility on the operator than on the vehicle itself in terms of mitigating risks.
Open Standards
Trusted standards drive Mobility as a Service in smart cities
Users are increasingly transferring their digital service expectations to public transport. For example, route planning services are more and more integrated with hotel booking systems and connecting transport ticketing facilities. This means, travelers need transparent and trusted open standards which will enable public transport operators (PTO) and authorities (PTA) to deploy secured, convenient and interoperable transport ticketing solutions.
Infineon’s commitment to open standards allows us to meet the specific needs of any public transport operator or authority. Specifications independently developed by a range of bodies within the transport community provides resilience and flexibility for the future while putting the PTO or PTA in control and avoiding vendor lock-in. That way, municipal governments can adopt technologies to create sustainable smart cities: Citizens digitally connect with city infrastructures in their daily lives and enjoy higher levels of convenience across multiple adjacent services. This creates significant opportunities for digital-based ticketing and smart mobility.

What's an open standard?
An open standard is publicly available and can be used by any market player. Open standards have equal, transparent terms and conditions – more commonly known as reasonable and non-discriminatory terms. Ideally, an independent body certifies open standard products, and all industry players are free to join the standardization body and contribute to the standardization process.
Payment systems
Secured and convenient payments systems

Digital payments are already clearly a part of our daily business and come with several benefits, e.g. no dependency on cash, fast transfer speed, easy handling and orientation to customer needs. To make the most of these benefits, consumers must be able to trust the technology, to access their money and purchase goods and services whenever they want to. When talking about the practical implementation of Mobility as a Service (MaaS), the payment system is a particular focus topic. For example, paying to charge electric cars is much more complex than paying at the gas station. The process of charging an electric vehicle at a charging point must also include the identification, authentication and safeguarding of information that passes between the charger, the vehicle, and the backend infrastructure.
E-Ticketing
Shaping the mobility experience with e-ticketing

Services such as contactless cards and mobile ticketing based on NFC (Near Field Communication) using smartphones already have been widely adopted. Contactless technologies are used for public transport, shared cars, bikes and e-scooters. Users hold their chip-based card to a reader terminal in order to securely authenticate or make a contactless and cashless payment. Travelers keep their e-tickets ready on the mobile phone digitally and tap the mobile device on the NFC reader when boarding the bus or train. These multi-modal services call for new, more robust, and faster security solutions. In this case once again semiconductors by Infineon provide state of the art solutions, capable of protecting passenger credentials and saving operators costs.
Ultra-wideband technology (UWB)
Increasing IoT device accuracy and positioning
Ultra-Wideband technology is on the rise in connection with the Internet of Things. This time of flight (ToF) based technology operates at frequencies between 3.1 and 10.6 GHz using wide channels of 500 Mhz and short 2 nanoseconds impulses. This combination allows a precise localization of devices with centimeter accuracy and thus smartly complements with other connectivity technologies such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth or NFC as well as with secure elements wherever required. The most important applications are hands-free access control for cars, garages and apartment doors, real-time location-based services such as application for augmented reality, indoor navigation or asset tracking. Other aspects are customized advertising, device-to-device services likes the localization of two smart phones, trackers or any other smart devices as well as smart home control.
The technology has breakthrough potential. Companies can use UWB wherever WiFi or Bluetooth with NFC (Near-Field Communication) are already in use. It could serve AR gaming, help with the orientation of autonomous cars, support delivery services with drones and make it easier to find friends in a given area. And finally, UWB may turn contactless Payment and Ticketing into a touchless experience without compromising security.
Security solutions
Creating trust in the possibilities of MaaS

Infineon has extensive expertise in building trusted solutions. We started to make security chips for phone cards more than 25 years ago. Today, hundreds of millions of Infineon chips in mobile phones, bank cards, ID cards and computers add more security to everyday life.
Products and solutions from Infineon play an essential role in securing financial transactions by protecting the authenticity of the entities involved, the integrity of the data exchanged and the confidentiality of sensitive information.
Our portfolio enables the breakthrough of Mobility as a Service (MaaS) in driving sustainable mobility – based on both digitalization and decarbonization.
Enabling a more seamless public transportation experience in South Africa – based on CIPURSE™
Public transportation in South Africa faces various challenges. The majority of train stations in South Africa have no gates, and the QR code paper tickets used are highly vulnerable to fraud, making fare evasion a widespread problem.
In addition to the trains, there are public buses and, most significantly, hundreds of thousands of minibus taxis carrying 15 to 20 million passengers every day. They account for the transportation of 69 % of South Africans. To make these different means of transportation more interoperable and to increase efficiency and performance, operators, transport authorities and customers have been calling for a single smartcard ticket solution for a long time.
Infineon is ready to meet this demand for multi-application cards with contactless functionality. Our products are based on the CIPURSE™ standard, which is driven by the international OSPT Alliance and enables the adoption of open standards in transportation ticketing. The CIPURSE™ standard allows interoperability across secured, cost-effective and flexible multi-application fare collection schemes. Infineon is the world’s first supplier of a complete CIPURSE™-certified product portfolio for secured, contactless cards supporting and combining public transportation ticketing, micro-payments, authentication and access.
Our CIPURSE™-certified products offer secured, hardware-based storage of AES-128 keys, enabling 3-pass mutual authentication and secured communication. Commands and data can be secured using the CIPURSE™ cryptographic protocol. In addition, our CIPURSE™-certified products are ideal for NFC applications running on standard infrastructures compliant with the NFC Forum Type 4 Tag Technical Specification.





